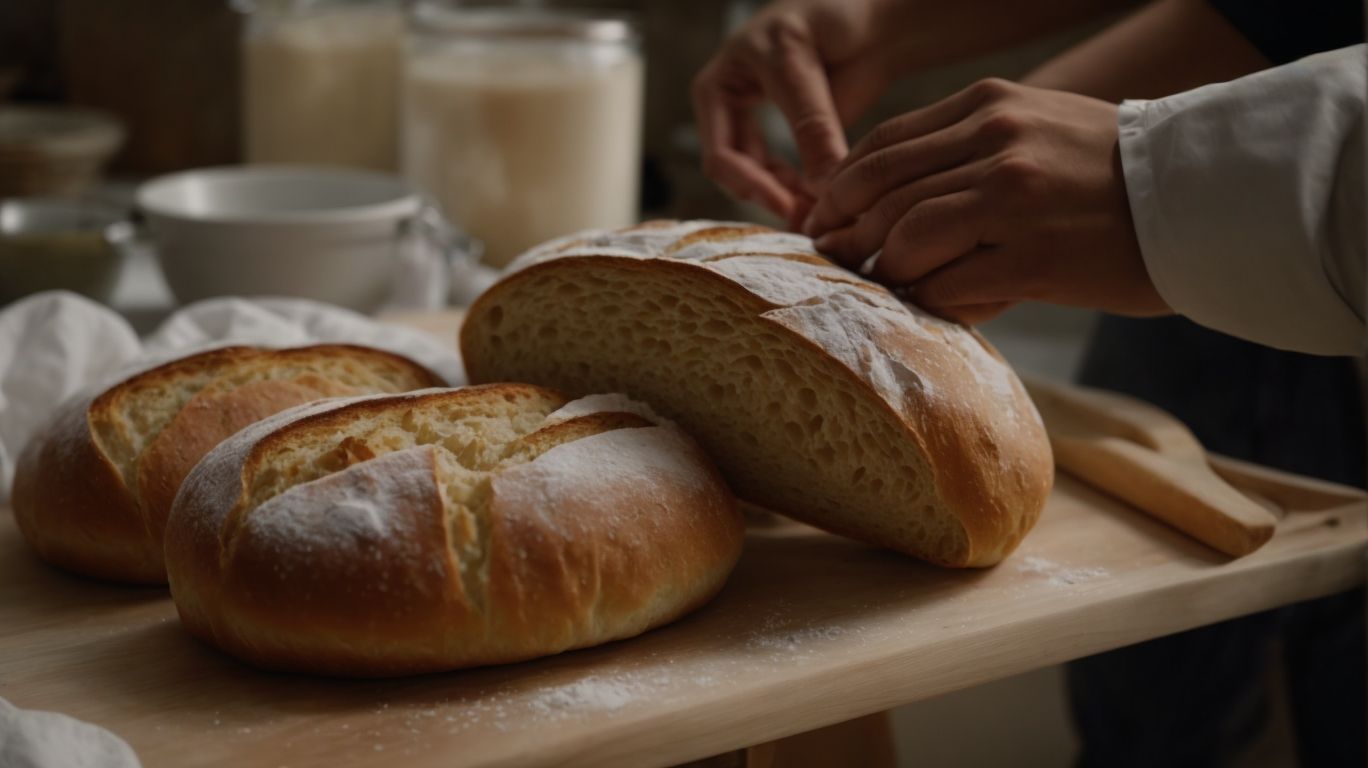
How to Bake With Yeast?
Yeast is a magical ingredient that plays a crucial role in baking, but do you really understand how it works?
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of yeast, its importance in baking, and the essential ingredients and equipment needed for successful yeast baking.
From activating yeast to using it in various baking methods, we will cover everything you need to know to master the art of baking with yeast.
Get ready to elevate your baking skills and impress your friends and family with delicious homemade breads and pastries!
Key Takeaways:
What is Yeast and How Does it Work?
Credits: Poormet.Com – Noah Campbell
Yeast, particularly Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a microorganism crucial in the process of fermentation, commonly used in baking to leaven bread and produce carbon dioxide gas.
When yeast is added to dough, it feeds on sugars present in the flour, breaking them down into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation. The carbon dioxide gas forms bubbles in the dough, which gets trapped, causing it to expand and rise during baking. This rise creates air pockets within the bread, contributing to its light and fluffy texture.
Yeast also plays a vital role in developing the flavor profile of bread, imparting that distinctive taste that we all associate with freshly baked goods. Its ability to release enzymes that break down complex carbohydrates not only aids in the fermentation process but also enhances the overall nutritional value of the bread.
What Are the Different Types of Yeast?
In terms of baking, there are several types of yeast available, including baker’s yeast, fresh yeast, instant yeast, and popular brands like Red Star, Fleischmann’s, and SAF.
Baker’s yeast, also known as active dry yeast, is the most common type used by home bakers for making bread, pizza dough, and other baked goods. It is readily available in small packets or jars and has a longer shelf life when stored in a cool, dry place. Fresh yeast, often found in the refrigerated section of specialty stores, provides a more pronounced flavor and is ideal for traditional bread recipes.
Instant yeast, also called rapid-rise or quick-rise yeast, is a convenient option for those who prefer minimal proofing time. This type is formulated to allow for faster fermentation, suitable for busy bakers or those looking for quick bread-making processes. Popular brands like Red Star, Fleischmann’s, and SAF offer a range of yeast products tailored to specific baking needs.
How Does Yeast Help in Baking?
Yeast aids in baking by initiating the fermentation process, leading to the rise of dough and the development of gluten structure, resulting in a well-textured loaf of bread.
During fermentation, yeast consumes sugars present in the dough, producing carbon dioxide gas and alcohol as byproducts. This gas gets trapped in the dough, causing it to expand and become airy. As the dough rises, the gluten network within it stretches, forming a strong and elastic framework that holds the gas bubbles. This process is crucial in giving bread its characteristic texture and structure.
The activity of yeast also influences the flavor profile of the baked goods, imparting a slightly tangy and complex taste due to the fermentation. Proper handling and proofing of dough with yeast are essential to achieve the desired texture and flavor in the final product.
What Ingredients Do You Need for Baking With Yeast?
To create delicious baked goods using yeast, essential ingredients such as water, sugar, and flour are combined according to a specific recipe.
Plus water, sugar, and flour, yeast-based baking requires yeast as the key leavening agent that helps the dough rise by fermenting the sugars found in the recipe. Yeast is a living organism that reacts with sugars and releases carbon dioxide gas, creating lightness and texture in the final baked product.
The role of salt in yeast-based dough is crucial; it helps control yeast fermentation, strengthens gluten development, and enhances the overall flavor of the baked goods. Without the right amount of salt, the dough’s texture and taste can be negatively affected.
Another important ingredient in yeast-based baking is fat, often in the form of butter or oil. Fat tenderizes the dough, adds richness, and contributes to the structure and moisture retention of the final baked items.
What Are the Essential Ingredients?
The essential ingredients for baking with yeast include water for hydration, sugar for yeast activation, and flour for structure and texture.
Water plays a crucial role in providing the necessary moisture for yeast to activate and begin fermentation, which is essential in dough rising. Without adequate hydration, yeast cannot properly metabolize sugars, leading to poor dough development.
Sugar acts as a food source for yeast, kickstarting its activity and promoting fermentation. It not only fuels the yeast cells but also contributes to the overall flavor and browning of the final baked product.
Flour, on the other hand, serves as the backbone of the dough, providing the necessary structure by developing gluten when kneaded. Gluten gives the dough its elasticity and strength, allowing it to trap gases released by the yeast and expand during proofing and baking.
What Are the Optional Ingredients?
While the essential ingredients are crucial, optional additions such as yeast cells, beneficial bacteria, and carbon dioxide enhancers can further enhance the flavor and texture of the final baked product.
Incorporating enzyme-rich components like malted barley flour or diastatic malt powder in yeast-based recipes can significantly contribute to dough fermentation by breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, aiding in the development of a robust gluten network for improved structure and volume.
The integration of vitamin C or ascorbic acid can act as a dough strengthener, promoting better gas retention during fermentation, resulting in a finer crumb and increased overall volume of the baked goods.
What Equipment Do You Need for Baking With Yeast?

Credits: Poormet.Com – Aaron Young
Plus ingredients, essential equipment such as mixing bowls, measuring cups, and proofing baskets are necessary for working with yeast to create perfectly risen dough and flavorful bread.
Having the right tools for yeast-based baking is crucial for achieving professional-quality results.
- Mixing bowls of various sizes allow you to combine ingredients and knead the dough without spilling, ensuring proper incorporation of yeast for optimal fermentation.
- Measuring cups help maintain accuracy in ingredient quantities, especially crucial for yeast activation.
- Proofing baskets, also known as bannetons, support the dough during its final rise, shaping it into a beautiful form while enhancing the bread’s texture and crust.
What Are the Basic Tools Required?
Basic tools for baking with yeast include a recipe for guidance, a reliable timer for precise timing, and a thermometer to monitor dough temperature during fermentation.
When diving into the world of yeast-based baking, it’s crucial to have these tools close at hand to ensure successful results. A recipe acts as your roadmap, guiding you through the right proportions of ingredients and detailed steps to follow. A dependable timer becomes your trusted assistant, helping you keep track of crucial rising and resting times. Meanwhile, a thermometer plays a vital role in maintaining the ideal temperature for the dough to ferment properly, ensuring that yeast activity is optimal.
What Are the Optional Tools That Can Make Baking Easier?
Optional tools like gluten enhancers, gas release mechanisms, and specialized bread pans can streamline the baking process, resulting in improved texture, flavor, and appearance of bread.
For instance, incorporating dough conditioners can help in optimizing the gluten structure, resulting in better crumb structure and overall texture of the bread. These additives aid in strengthening the dough and promoting a more consistent rise during proofing.
Utilizing steam injection ovens can enhance gas retention within the dough, leading to a lighter and fluffier loaf. By controlling the amount of steam during the baking process, bakers can achieve that coveted crispy crust without compromising the soft interior.
Investing in couche cloths can assist in shaping loaves, especially helpful when working with high-hydration doughs. These cloths support the dough during the final rise, helping maintain the desired shape and structure before transferring to the oven.
How to Activate Yeast?

Credits: Poormet.Com – Logan King
Activating yeast involves initiating the fermentation process by providing a warm environment, suitable sugar source, and yeast cells to kickstart the growth and gas production.
Creating optimal fermentation conditions is crucial for activating yeast effectively. Ensure the warm environment is between 110-115°F to activate the yeast without killing it. Utilize sugar sources like honey, malt extract, or plain sugar to provide the necessary energy for yeast metabolism.
- Next, check the yeast’s viability by proofing it in warm water with a pinch of sugar.
- Look for signs of activity, such as bubbling or foaming, indicating live yeast cells.
- By following these steps, you can ensure a healthy and active yeast for proper dough leavening.
What Are the Steps to Activate Yeast?
The process of activating yeast involves proofing it in warm water with a pinch of sugar, allowing it to bloom for a specific time until it shows signs of rise and fermentation activity.
One crucial element in activating yeast effectively is to use water at the right temperature, typically between 100°F to 110°F, as water that is too hot can kill the yeast, while water that is too cold may not activate it efficiently.
After the yeast is added to the warm water and sugar mixture, it is essential to let it sit undisturbed for about 5-10 minutes to allow the yeast to activate and start fermenting. This step is known as proofing, where the yeast consumes the sugar and releases carbon dioxide, causing the mixture to bubble and rise.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Activating Yeast?
Common mistakes when activating yeast include using overly hot water, neglecting proofing time, or combining yeast directly with salt or high-sugar ingredients, which can hinder proper fermentation and dough development.
Water temperature control is crucial during yeast activation. If the water is too hot, it can kill the yeast, leading to failed fermentation. On the other hand, water that is too cold may not activate the yeast efficiently.
Consistency in proofing is also essential. Allowing the dough to proof for the specified time ensures that the yeast has enough time to work its magic. Skipping this step can result in dense and underdeveloped bread.
It’s important to be mindful of ingredient compatibility. Yeast should not come into direct contact with salt or high-sugar ingredients like honey or molasses before mixing with other ingredients, as these can inhibit yeast activity.
By understanding and avoiding these common errors, you can make sure your yeast-based recipes rise to perfection.
How to Use Yeast in Baking?

Credits: Poormet.Com – Sean Rivera
Utilizing yeast in baking involves following a precise recipe, allowing dough to ferment adequately, and shaping the loaf before the final proofing stage to achieve a well-textured and flavorful bread.
In terms of incorporating yeast into your baked goods, accuracy is key.
Measuring the yeast precisely
ensures the right amount of leavening agent for optimal rise and structure. Temperature plays a crucial role in the fermentation process. Yeast thrives in a warm, but not overly hot environment, so finding the perfect spot for your dough to rise is essential. Attentive
dough handling techniques
also contribute to the final product. Kneading the dough properly helps develop gluten for that desired chewy texture, while gently shaping the loaf ensures an even rise during baking.
What Are the Different Methods of Using Yeast in Baking?
Various methods of using yeast in baking include traditional proofing with warm water, cold fermentation for enhanced flavor development, and sugar-activated rapid rise techniques for quick bread preparation.
Traditional proofing is a fundamental technique where yeast is dissolved in warm water, allowing it to activate and start fermenting, leading to the expansion of dough. This process not only aids in leavening but also imparts a distinct flavor to the final baked product.
On the other hand, cold fermentation involves a prolonged resting period in the refrigerator, which intensifies the flavors in the dough and contributes to a richer taste profile.
Sugar-activated rapid rise methods are essential for those seeking fast results, as the added sugar boosts yeast activity, enabling the dough to rise swiftly.
What Are the Dos and Don’ts of Using Yeast in Baking?
Dos of using yeast in baking include allowing sufficient fermentation time, kneading dough for gluten development, and monitoring gas production, while don’ts involve overproofing, excessive sugar content, and improper loaf shaping that can affect the final bread quality.
Proper temperature control during fermentation is crucial for yeast activity. Avoid placing the dough in extremely hot or cold environments as it can hinder the fermentation process. Yeast viability is impacted by temperature extremes.
Ensure you use fresh yeast or activate dried yeast properly to maximize its effectiveness in raising the dough.
When shaping your bread, don’t forget to gently handle the dough to prevent degassing, which can lead to a dense final texture. Using a gentle touch promotes aeration and a desirable crumb structure in the finished loaf.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Bake With Yeast?
What is yeast and why is it used in baking?
Yeast is a type of fungus that is commonly used in baking to help dough rise and give bread its airy texture.
Can I use any type of yeast in my baking?
There are different types of yeast, such as active dry yeast, instant yeast, and fresh yeast. Each type has different properties and should be used according to the recipe’s instructions.
How do I activate yeast before using it in my recipe?
To activate yeast, mix it with warm water and a pinch of sugar. Let it sit for 5-10 minutes until it becomes foamy. This step ensures that the yeast is active and will help your dough rise.
How to Bake With Yeast?
How do I know if my yeast is still good?
To test if your yeast is still active, mix it with warm water and a pinch of sugar. If it becomes foamy within 5-10 minutes, it is still good to use. If not, it may be expired and should be replaced.
Can I use alternative ingredients instead of yeast in my baking?
Yes, there are alternatives to yeast such as baking powder or baking soda. However, each ingredient has different properties and may result in a different texture in your baked goods.
How do I store yeast for future use?
Yeast should be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator or freezer to keep it fresh. Make sure to check the expiration date before using it in your baking.

